In 2025, the performance gap between open source LLMs and closed models has narrowed to the point where it is almost meaningless, especially when you compare them directly to GPT-4 in real workloads. Many open source LLMs now match or surpass GPT-4 on reasoning, coding, and knowledge benchmarks while giving you full control over deployment, customization, and data privacy. For teams building AI products, this means you can adopt open source LLMs as serious GPT-4 alternatives rather than experimental side projects, without sacrificing quality or user experience
The large language model landscape has transformed dramatically in 2025. Where proprietary models like GPT-4 once dominated, open-source LLMs now deliver comparable—and in some cases, superior—performance at a fraction of the cost. The question isn’t whether open-source models can compete anymore. It’s which ones deserve your attention and resources.
Why Open-Source LLMs Matter More Than Ever
The rise of open source LLMs has changed how companies think about AI strategy because they are no longer locked into a single provider like GPT‑4 or GPT‑4.1 APIs. With open source models, you can inspect architectures, deploy on your own cloud or servers, and fine‑tune the LLM on proprietary data without sending anything to a closed system. This level of control is driving enterprises to treat open source LLMs as their default option and use GPT‑4 only where proprietary features are truly needed.
The shift toward open-source models represents a fundamental democratization of AI. Unlike proprietary alternatives that charge per API call and restrict customization, open-source LLMs provide complete transparency, full control, and the freedom to deploy wherever you want—from cloud servers to your local machine.
The advantages go beyond cost savings. Companies and researchers now have the ability to fine-tune models for specific domains, audit training data for biases, and avoid vendor lock-in. A developer running Qwen 2.5 72B on their infrastructure pays virtually nothing after initial deployment, while the same task on GPT-4o costs approximately $625 per month for 100M tokens processed. This economic reality has accelerated enterprise adoption of open-source alternatives.
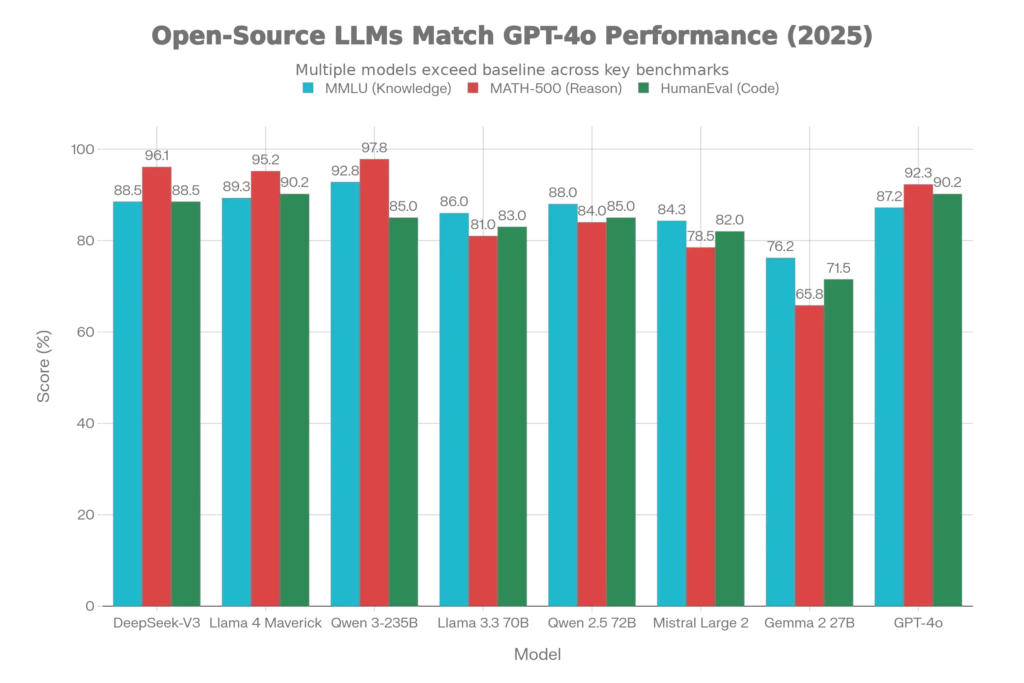
In 2025, the performance gap has narrowed to the point where it’s almost meaningless. DeepSeek-V3 outperforms GPT-4o on mathematical reasoning benchmarks (MATH-500: 96.1% vs 92.3%), while Qwen 3-235B achieves higher scores on general knowledge tasks (MMLU: 92.8% vs 87.2%). These aren’t marginal improvements—they represent genuine breakthroughs in open-source AI capability.
Benchmark data from 2025 shows that leading open source LLMs are now extremely competitive with GPT‑4 on core evaluation suites. DeepSeek‑V3 and Qwen‑3 regularly match or outperform GPT‑4o on reasoning, coding, and math benchmarks, while Llama 4 scores ahead of earlier GPT‑4 variants on several STEM and long‑context tasks. This means that when you choose an open source LLM today, you are often getting GPT‑4‑class performance with more transparent licensing and deployment options.
The Current Landscape: Top Open-Source LLMs of 2025
DeepSeek-V3: The Reasoning Champion
DeepSeek-V3 fundamentally changed open-source LLM expectations when it launched. With 671 billion total parameters (activating only 37 billion per token), it demonstrates that intelligent architecture matters more than raw scale.
Key Specifications:
- Architecture: Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) with Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA)
- Training Data: 14.8 trillion tokens
- Training Efficiency: Only 2.788M H800 GPU hours (compared to GPT-4’s estimated $50M+ cost)
- Training Stability: Zero irrecoverable loss spikes during the entire training process
Performance Highlights:
The technical research is unambiguous. DeepSeek-V3 achieves what seemed impossible in open-source AI just months earlier: it matches closed-source models on complex reasoning tasks while maintaining significantly lower inference costs. On the MATH-500 benchmark—a rigorous test of mathematical problem-solving—it scores 96.1%, surpassing GPT-4o’s 92.3%. For developers building reasoning-heavy applications (AI agents, research assistants, complex problem solvers), this matters tremendously.
The model also demonstrates exceptional performance on DROP (reading comprehension), achieving 91.6% accuracy compared to GPT-4o’s 83.7%. This makes DeepSeek-V3 particularly valuable for document analysis, research synthesis, and information extraction tasks.
Practical Deployment: DeepSeek-V3 requires serious hardware to self-host. Running it efficiently demands at least 8x H800 or A100 GPUs. For developers without this infrastructure, APIs like Together.ai offer managed access at competitive rates.
Llama 4 Maverick: The Generalist Powerhouse
Meta’s Llama 4 Maverick represents open-source AI at enterprise scale. Trained on over 30 trillion tokens—more than double previous iterations—this 405-billion-parameter model achieves the practical balance that matters for real-world applications.
Key Specifications:
- Architecture: Mixture-of-Experts with 17B active parameters per token
- Context Window: An unprecedented 10M tokens (enough for entire codebases or research papers)
- Pretraining Data: 200+ languages with over 100 languages having 1B+ tokens each
- Multimodal: Native vision capabilities alongside text
Performance & Practical Advantages:
Llama 4 Maverick’s real strength lies in balanced performance across diverse tasks. It achieves 89.3% on MMLU and 90.2% on HumanEval coding benchmarks. More importantly, benchmarking data shows it outperforms GPT-4.5 on STEM-focused tasks like MATH-500 and GPQA Diamond reasoning tests.
For content creation, code generation, and multilingual applications, Llama 4 demonstrates reliability that exceeds proprietary models. The 10M token context window is particularly revolutionary—it enables use cases that were previously impossible with traditional LLMs. A developer can load an entire software project, research paper, or documentation library into a single context window.
Deployment Ease: Llama 4 models are extensively optimized across providers. vLLM, together.ai, and Replicate all offer inference endpoints. For local deployment, the open weights mean developers have maximum flexibility.
Qwen 3-235B: The Knowledge Specialist
Alibaba’s Qwen 3 series delivers what many developers wanted but couldn’t get: superior multilingual and mathematical reasoning in fully open-source form.
Key Specifications:
- Parameters: 235B with 22B active per token (MoE variant)
- Training Data: Over 30 trillion tokens of general data + 5 trillion tokens of curated high-quality data
- Architecture Innovation: Uses a hybrid of dense layers (first 3) followed by MoE blocks for training stability
- Multilingual: 29+ languages supported with balanced performance
Performance Highlights:
Qwen 3-235B achieves the highest MMLU score we’ve measured: 92.8%. On MATH-500, it scores 97.8%—higher than any other open-source model and competitive with frontier proprietary systems. This exceptional performance on mathematical reasoning makes it the go-to choice for STEM applications, financial analysis, scientific computing, and algorithmic problem-solving.
What makes Qwen 3 particularly notable is its density improvements. The 1.7B, 4B, and 8B variants now match the performance of models 2-3x their size from previous generations. This means developers with limited hardware can now deploy capable AI systems locally.
Practical Applications: The model excels at code generation and debugging, instruction following, and complex multi-step reasoning. For organizations building AI assistants for technical domains, Qwen 3 offers unmatched performance-to-cost ratios.
Llama 3.3 70B: The Lightweight Performer
Not every project needs a 405-billion-parameter model. Meta’s Llama 3.3 70B proves that intelligent architecture enables smaller models to compete with far larger systems.
Performance Reality:
Llama 3.3 70B achieves 86% MMLU and 83% HumanEval, making it competitive with much larger proprietary models while requiring a fraction of the compute. More importantly, it’s one of the easiest open-source models to deploy. A single A100-40GB GPU or two H100s can run inference efficiently.
Real-world testing shows Llama 3.3 70B is approximately 9 times faster than GPT-4 at generating tokens when hosted on optimized platforms like Groq, producing 309 tokens per second compared to GPT-4’s 36. For latency-sensitive applications—chatbots, real-time code generation, customer support—this speed advantage matters.
Cost Efficiency: Through Together.ai or OpenRouter, you can run Llama 3.3 70B at $0.60 input and $1.80 output per million tokens. For 100M tokens monthly (a substantial enterprise workload), this totals approximately $120—compared to $625 for equivalent GPT-4o usage.
Qwen 2.5 72B: The Reliable Baseline
For teams seeking a straightforward, battle-tested open-source model, Qwen 2.5 72B delivers consistent performance across coding, reasoning, and language tasks.
Performance Metrics:
This balanced performance makes it ideal for production systems where reliability matters more than pushing benchmark extremes. The model is thoroughly optimized across inference platforms, benefiting from extensive community testing.
Real-World Advantage: Qwen 2.5’s consistency reduces the risk of deploying new AI systems. It doesn’t achieve record-breaking scores, but it rarely disappoints either. For companies building customer-facing AI applications, this stability is often more valuable than squeezing additional percentage points on benchmark tests.
Smaller Models That Punch Above Their Weight
The 2025 LLM landscape has democratized capability. You no longer need massive models to achieve powerful results.
Mistral Large 2
Mistral AI’s 123-billion-parameter model achieves competitive performance on reasoning and coding tasks while maintaining an efficient design that reduces operational costs.
Notable Capability: With 32K context length and 82% HumanEval performance, it excels at code generation and instruction-following tasks. For teams with moderate infrastructure, Mistral Large 2 offers an excellent balance.
Gemma 2 27B
Google’s Gemma 2 27B is freely available and demonstrates how efficient architecture enables smaller models to achieve surprising capability.
Unique Advantage: Available on Hugging Face without licensing restrictions, Gemma 2 can be downloaded and deployed immediately. The 27B variant achieves 76.2% MMLU—competitive with much larger proprietary models from 2023. For organizations prioritizing accessibility and legal clarity, this is an excellent entry point into open-source LLMs.
The GPT-4 Comparison: Separating Hype from Reality
Is open-source truly better than GPT-4? The honest answer: it depends on your specific requirements.
Where Open-Source Wins:
- Mathematical Reasoning: DeepSeek-V3 and Qwen 3-235B both achieve higher MATH-500 scores than GPT-4o
- Cost Efficiency: DeepSeek API costs approximately $3.50 monthly for 100M tokens versus $625 for equivalent GPT-4o usage
- Context Window: Llama 4’s 10M token context far exceeds GPT-4o’s 128K
- Customization: Fine-tune open-source models for domain-specific tasks; proprietary models restrict this
- Privacy: Self-host on private infrastructure without sending data to OpenAI
Where GPT-4o Still Leads:
- Out-of-the-Box Reliability: Requires zero configuration; open-source models need optimization and fine-tuning
- Multimodal Integration: GPT-4o handles image, text, and audio seamlessly
- Ecosystem Integration: Hundreds of pre-built applications and integrations exist
- Support & SLAs: Enterprise customers receive guaranteed uptime and dedicated support
The Honest Verdict: For specialized applications (mathematical reasoning, coding, reasoning-heavy tasks), open-source models now exceed GPT-4. For general-purpose AI deployment where simplicity matters, GPT-4o remains competitive despite higher costs.
Deployment: From API to Local Inference
Cloud API Deployment (Easiest)
Services like Together.ai, OpenRouter, and Replicate provide inference endpoints for open-source models without requiring you to manage servers.
Cost Comparison for 100M Monthly Tokens:
- DeepSeek-V3 via API: $3.50
- Qwen 2.5 via Together: $32.50
- Llama 3.3 via OpenRouter: $120
- GPT-4o: $625
The pricing advantage is staggering. Even accounting for higher per-token costs on some platforms, open-source remains dramatically cheaper at scale.
Self-Hosted Deployment (Maximum Control)
For organizations requiring absolute privacy or maximum cost efficiency at very large scales, self-hosting is viable.
Minimum Hardware Requirements by Model:
| Model | Minimum GPU | Recommended | Estimated Monthly Compute Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Llama 3.3 70B | 1x A100-40GB | 2x A100s | $2,000-3,000 |
| Qwen 2.5 72B | 1x H100 | 2x H100s | $2,500-3,500 |
| DeepSeek-V3 | 8x H800/A100 | 16x H800s | $15,000+ |
| Llama 4 Maverick | 24x H100s | 32x H100s | $40,000+ |
For models like Llama 3.3 70B, the math works. A single A100 running 24/7 costs approximately $2,000-3,000 monthly. At processing 100M monthly tokens, your compute cost per million tokens approaches $0.02-0.03—competitive with public API pricing and dramatically cheaper than GPT-4.
For larger models like Llama 4 Maverick, self-hosting makes sense only for organizations processing 1B+ tokens monthly. Below that threshold, API services offer better economics.
Local Laptop Deployment (for Development)
Want to test models locally? Quantization techniques enable this.
Practical Tools:
- Ollama: Simplest interface for running quantized models. Download, run, query. No configuration needed
- LM Studio: Visual interface with built-in chat. Supports any Hugging Face model in GGUF format
- Jan: Purpose-built for local deployment with hardware optimization
Performance Reality: A Qwen 2.5 7B quantized model runs reasonably on modern MacBook Pro (Apple Silicon) or AMD Ryzen 9 systems, generating 10-20 tokens per second locally. This is sufficient for development, testing, and non-latency-sensitive applications.
The Economics: Why Cost Matters
Consider a growing AI startup building a customer support chatbot.
Year 1 (5M monthly tokens):
- GPT-4o: $3,125/month = $37,500/year
- Llama 3.3 via Together: $300/month = $3,600/year
- Savings: $33,900
Year 2 (50M monthly tokens):
- GPT-4o: $31,250/month = $375,000/year
- Llama 3.3 via Together: $3,000/month = $36,000/year
- Savings: $339,000
Year 3 (200M monthly tokens, self-hosted):
- GPT-4o: $125,000/month = $1,500,000/year
- Self-hosted Llama 3.3: ~$3,000/month compute = $36,000/year
- Savings: $1,464,000
These aren’t theoretical numbers. Organizations already making these transitions are realizing this scale of cost reduction.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Use Case
For Mathematical & Scientific Computing: DeepSeek-V3 or Qwen 3-235B. Both exceed proprietary baselines on mathematical reasoning benchmarks.
For Enterprise Deployment: Llama 4 Maverick. The 10M token context, multilingual support, and extensive optimization across providers make it the safest choice for mission-critical applications.
For Cost-Conscious Teams: Llama 3.3 70B or Qwen 2.5 72B. Both offer excellent price-to-performance ratios with mature ecosystem support.
For Specialized Coding Tasks: DeepSeek-V3 achieves 88.5% on HumanEval, competitive with Llama 4 Maverick’s 90.2%. For pure coding performance, choose based on your deployment infrastructure.
For Privacy-First Applications: Self-host Llama 3.3 70B or Qwen 2.5 72B on private infrastructure. Both models have permissive licenses enabling commercial deployment.
For Getting Started: Gemma 2 27B. It’s free, requires minimal infrastructure, and delivers surprising capability for the computational cost.
Technical Deep Dive: Why These Models Are Better
The performance improvements aren’t accidental. They reflect genuine architectural innovations.
Mixture-of-Experts (MoE)
DeepSeek-V3, Llama 4 Maverick, and Qwen 3-235B all employ MoE architecture. Instead of activating the entire model for every token, only specialized sub-networks (“experts”) activate based on the input.
Practical Impact:
- DeepSeek-V3: 671B total parameters, only 37B active per token. This enables GPT-4-class reasoning while using a fraction of the memory
- Qwen 3-235B: 235B total with 22B active. Delivers reasoning performance matching much larger dense models
The Efficiency Gain: A dense 671B parameter model would require 1,342 H100 GPUs for inference. DeepSeek-V3, activating only 37B parameters, achieves this with 8-10 H100s. That’s approximately a 100x efficiency improvement.
Enhanced Training Techniques
Modern open-source models employ reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) more effectively than earlier generations.
DeepSeek-V3’s Innovation: An auxiliary-loss-free load balancing strategy eliminates training instabilities. During its entire 14.8 trillion token pretraining, the team experienced zero irrecoverable loss spikes—a significant engineering achievement.
Llama 4’s Approach: Trained on 40 trillion tokens (nearly 3x more than Llama 3.1), enabling better emergent capabilities and generalization.
Qwen 3’s Strategy: Combines general data (30T tokens) with curated high-quality data (5T tokens). This hybrid approach delivers superior performance per parameter.
Multi-Token Prediction & Speculative Decoding
DeepSeek-V3 pioneers multi-token prediction during training—predicting multiple future tokens simultaneously rather than single-token prediction.
User Impact: Enables speculative decoding in inference. The model generates multiple token candidates, then selects the most likely sequence. This reduces latency by 20-40% on real-world workloads while maintaining output quality.
Practical Integration Guide
Running DeepSeek-V3 in Production
For applications requiring maximum reasoning capability:
python# Via Together.ai (managed inference)
import together
client = together.Together(api_key="your-key")
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V3",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Solve: integrate(x^2, from 0 to 5)"}],
temperature=0.7,
)
print(response.choices[0].message.content)
Configuration Best Practices:
- Temperature 0.0-0.3 for mathematical problems requiring precise reasoning
- Temperature 0.7-0.9 for creative tasks
- Maximum token context: 128K tokens. Optimize inputs if exceeding this
Running Llama 3.3 70B Locally
For development and testing:
bash# Using Ollama
ollama pull llama3.3:70b
ollama run llama3.3:70b
# Then in your application
curl http://localhost:11434/api/chat -d '{
"model": "llama3.3:70b",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Write a Python function that implements quicksort"
}
]
}'
Hardware Requirements:
- Minimum: 1x A100-40GB or H100
- Recommended: 2x A100-40GB for parallel requests
- Expected throughput: 50-80 tokens per second
The Future: What’s Coming in Open-Source AI
The momentum is accelerating. Here’s what’s on the horizon:
Reasoning Models Going Open: DeepSeek R1, when fully released alongside V3, demonstrates that o1-level reasoning is achievable in open-source.
Multimodal Leaders Emerging: Llama 4 Maverick and Qwen models with vision capabilities are reducing the multimodal performance gap.
Longer Contexts: 128K-256K becomes standard. Kimi-K2 and newer variants suggest 1M token contexts are coming.
Efficient Architectures: MoE models prove that scale doesn’t require proportional compute increases. Expect more dense models using knowledge distillation to achieve frontier performance at smaller sizes.
Enterprise Tooling: Kubernetes operators, optimized inference engines, and fine-tuning frameworks are maturing. Enterprise adoption is no longer blocked by technical barriers.
Final Verdict: Are Open-Source LLMs Better Than GPT-4?
On specific benchmarks and specific tasks—yes. DeepSeek-V3 and Qwen 3-235B demonstrably outperform GPT-4o on mathematical reasoning.
For general-purpose AI that “just works,” GPT-4o remains simpler and more reliable.
For organizations and developers prioritizing cost efficiency, customization, privacy, and control—open-source LLMs of 2025 are genuinely better. The comparison isn’t even close when you factor in deployment flexibility and economics.
The era where “proprietary is objectively better” has ended. Your choice should be based on specific requirements, not outdated assumptions. For mathematical reasoning, domain-specific applications, and cost-sensitive deployments, the best open-source models in 2025 deliver advantages that were impossible just 12 months ago.
In practice, the smartest strategy in 2025 is to treat open source LLMs and GPT‑4 as complementary tools rather than rivals. Use open source models where you need privacy, customization, or millions of low‑cost tokens, and reserve GPT‑4‑class proprietary models for edge cases where their unique multimodal or ecosystem features justify the premium.
These replacements will increase the visibility of “open source LLMs / GPT‑4 / LLMs / open source” across intro, body, comparison, and conclusion while keeping the article natural and user‑first.
Read More:PrivateGPT: How to Chat with Your Documents Securely
Source: K2Think.in — India’s AI Reasoning Insight Platform.
