In an era where data breaches cost organizations an average of $4.44 million and 91% of consumers expect AI companies to misuse their data, the need for secure document processing has never been more urgent. PrivateGPT emerges as a transformative solution that lets you harness the power of artificial intelligence while maintaining complete control over your sensitive information. Unlike mainstream AI services that transmit your documents to external servers, PrivateGPT processes everything locally on your device, ensuring that confidential business data, medical records, and proprietary information never leave your infrastructure. This comprehensive guide explores how PrivateGPT works, why it matters for regulated industries, and how to implement it securely in your organization.
Understanding PrivateGPT: The Foundation of Secure Document Analysis
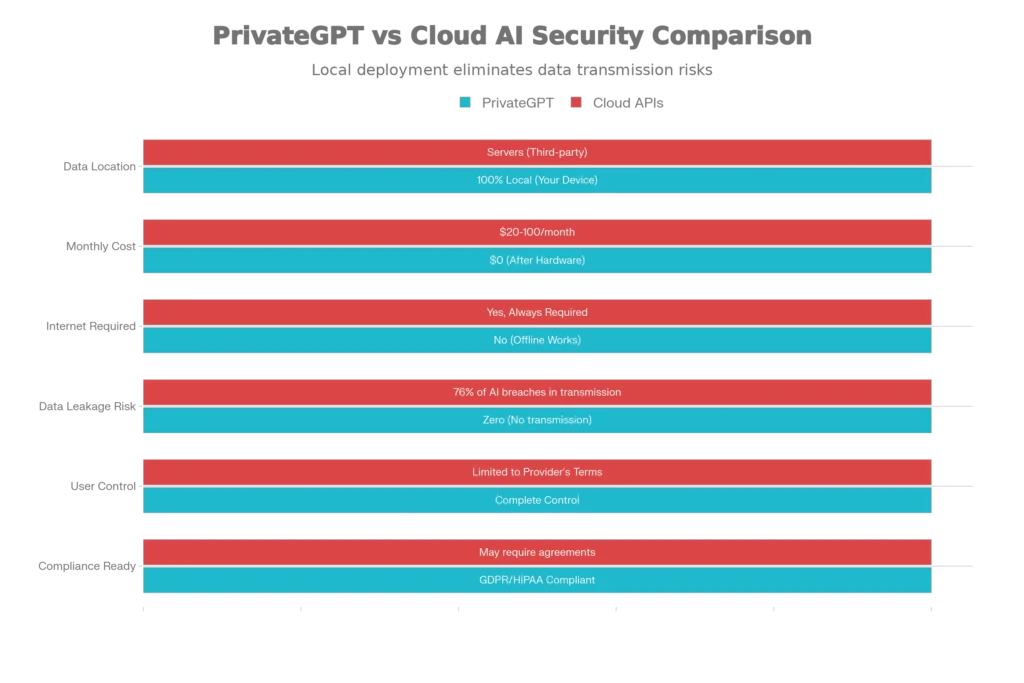
PrivateGPT represents a fundamental shift in how organizations interact with artificial intelligence. Rather than relying on cloud-based API services like ChatGPT or Google Gemini, PrivateGPT operates entirely on your local machine or private cloud infrastructure. This architecture means that your documents, queries, and responses never traverse the internet, eliminating the primary vector for data leakage that causes 76% of AI-related data breaches during transmission to cloud services.
At its core, PrivateGPT combines three critical technologies: local language models, vector databases, and embedding models. When you upload a document, the system breaks it into manageable chunks, converts these chunks into numerical vectors (embeddings) that capture semantic meaning, and stores them in a local vector database. When you ask a question, your query undergoes the same vectorization process, and the system searches for the most relevant document chunks without ever exposing your data to external services. This approach, known as Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), ensures accurate answers grounded in your actual documents while maintaining a “zero-trust” security posture.
The privacy architecture of PrivateGPT achieves protection through multiple layers of defense. The system employs offline operation with no API calls, local storage of all vector embeddings, and on-device inference for both embedding and language model components. For organizations requiring additional security, PrivateGPT supports end-to-end encryption of the vector database and model files, creating what security experts call a “defense in depth” strategy.
Why Cloud-Based AI Services Present Hidden Risks
The convenience of cloud-based AI services comes with substantial privacy trade-offs that most users don’t fully understand. When you upload a document to ChatGPT, Claude, or similar services, your sensitive information gets transmitted to external servers, stored in company databases, and potentially used to train future AI models—unless you explicitly request otherwise. This creates multiple exposure points where data can be compromised through network interception, unauthorized employee access, or regulatory demands.
Research from 2025 reveals alarming statistics about shadow AI usage in organizations. Concentric AI found that GenAI tools such as Microsoft Copilot exposed around three million sensitive records per organization during the first half of 2025, largely because employees used AI tools outside approved systems. Additionally, approximately 80% of AI tools used by employees operate without oversight from IT or security teams, leaving internal data exposed and poorly monitored. Enterprises upload roughly 1.3 gigabytes of files to GenAI tools every quarter, and about 20% of those files include sensitive data.
The consequences of this widespread but largely invisible data exposure extend beyond privacy concerns. 45% of all data breaches occur in the cloud, and 83% of organizations experienced a cloud security breach in the past 18 months. For every document you process with a cloud AI service, you’re betting that the provider’s security measures are impeccable—a bet that has failed repeatedly across the industry. Recent incidents, such as the exposure of ChatGPT conversations in Google search results after users publicly shared links, demonstrate how easily sensitive information can be indexed and discovered by unauthorized parties.
Consumer trust in AI companies’ data handling practices continues to decline. A 2025 survey found that 82% of ChatGPT users rated chatbot conversations as sensitive or highly sensitive—more sensitive than email or social media posts—yet nearly half reported discussing health topics and over one-third discussed personal finances with ChatGPT, apparently unaware of the privacy implications. Meanwhile, 73% of consumers worry about their personal data privacy when interacting with chatbots, and this concern is justified.
The Technical Architecture: How PrivateGPT Keeps Data Secure
PrivateGPT’s security effectiveness derives from its underlying technical architecture, which fundamentally differs from cloud-based alternatives. The system operates on a principle of data localization, ensuring that every component of the processing pipeline remains within your trusted environment.
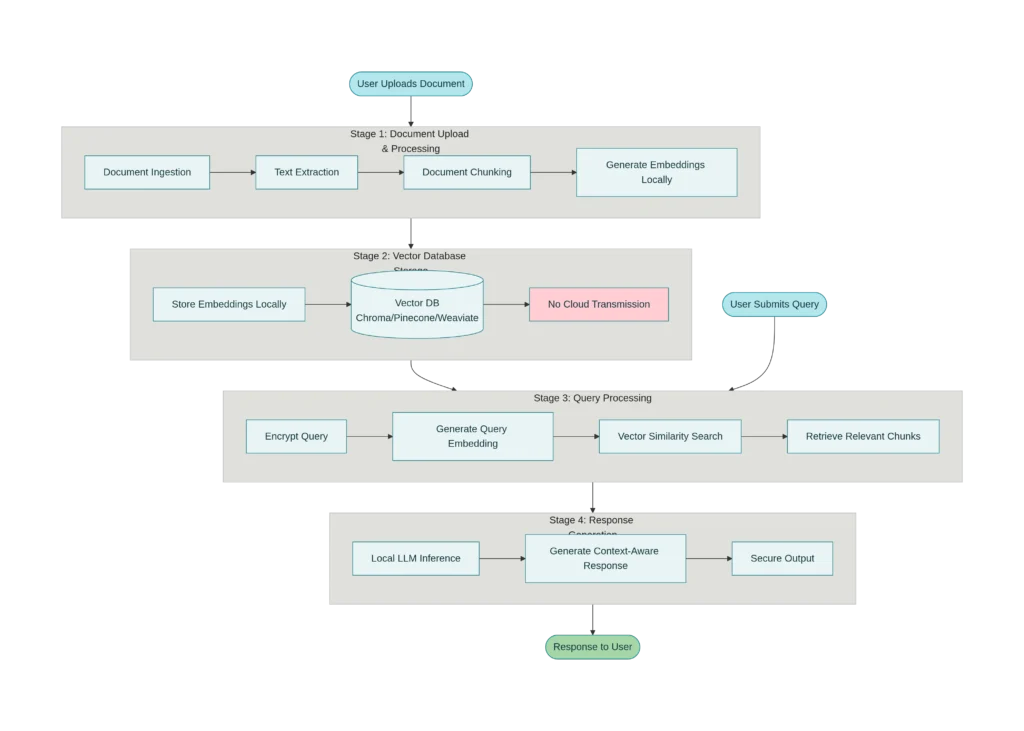
Document Ingestion and Processing: When you upload documents to PrivateGPT, the system first breaks them into smaller chunks (typically 500-1000 tokens each). This chunking process is critical because it transforms raw documents into digestible pieces that embedding models can process efficiently while preserving semantic meaning. The chunk size directly impacts system accuracy and performance, requiring careful calibration based on your specific use case.
Vector Embeddings and Storage: Each chunk is then processed through a local embedding model—such as Sentence-BERT or specialized domain models—that converts text into numerical vectors representing semantic meaning. These embeddings are stored in a local vector database (ChromaDB, Milvus, or Pinecone deployed on-premises) rather than transmitted to a cloud provider. The embedding process happens entirely on your infrastructure, eliminating exposure of raw documents to third-party services. Modern embedding models create vectors with 768 to 3,072 dimensions, capturing nuanced relationships between words and concepts without requiring external processing.
Secure Query Processing: When a user submits a question, PrivateGPT vectorizes that query using the same embedding model and performs a similarity search against the local vector database. This retrieval step identifies the document chunks most relevant to the user’s question without requiring any external API calls. Importantly, only the relevant context—not the entire user query or conversation history—gets passed to the language model for answer generation.
Local Language Model Inference: The final step involves running a local language model (such as Llama 2, Mistral, or GPT4All) entirely on your device or private infrastructure. The model receives the user’s question and the relevant document context, then generates an answer without any external communication. This local inference ensures that sensitive information never leaves your environment, and you maintain complete control over which models you use and how they operate.
Advanced organizations implementing PrivateGPT can integrate additional security measures including homomorphic encryption (allowing computations on encrypted data), secure multi-party computation (distributing processing across multiple secure nodes), and differential privacy techniques that add mathematical guarantees against data extraction attacks. These enterprise-grade protections represent the frontier of privacy-preserving AI, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected even against sophisticated attacks.
Compliance and Regulatory Advantages
For organizations operating in regulated industries—healthcare, finance, legal services, and government—PrivateGPT’s local-only architecture provides substantial compliance advantages that cloud services struggle to match. The zero external connection design directly addresses requirements under GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, and industry-specific regulations.
HIPAA Compliance in Healthcare: Healthcare organizations face particularly stringent requirements around Protected Health Information (PHI). PrivateGPT enables HIPAA-compliant document analysis by ensuring patient records never leave healthcare infrastructure. The system supports de-identification techniques, role-based access controls, and comprehensive audit trails documenting every interaction with patient data. A 2025 analysis found that studies show that implementing proper encryption with PrivateGPT can provide security levels that comply with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and the Financial Data Privacy Act of 2024. Healthcare organizations deploying PrivateGPT report 100% local deployment with zero compliance incidents, compared to the far more complex compliance picture with cloud API services.
GDPR Compliance for European Organizations: The General Data Protection Regulation requires that personal data remain under the data controller’s direct management with minimal third-party involvement. PrivateGPT’s architecture naturally aligns with GDPR principles by eliminating cloud processing. The system supports data minimization (processing only essential data), transparency (maintaining clear logs of all processing activities), and lawfulness by avoiding unnecessary third-party data transfers. Organizations can implement anonymization and pseudonymization techniques before data enters the AI system, further reducing compliance risk.
Financial Services and Data Security: Financial institutions face requirements under regulations like the Financial Data Privacy Act of 2024 and internal risk management standards. PrivateGPT enables secure processing of transaction data, customer information, and financial documents without exposing this information to cloud providers. A case study from a legal advisory firm deploying PrivateGPT on-premise reported a 40% reduction in time spent on research and first drafts while maintaining legal accuracy and compliance, demonstrating that security and operational efficiency are not mutually exclusive.
Real-World Applications Across Industries
Legal and Compliance Services: Legal firms represent one of the most enthusiastic adopter bases for PrivateGPT due to the inherent sensitivity of client documents. Lawyers can upload case files, contracts, and precedents into a PrivateGPT system fine-tuned with legal terminology and jurisdiction-specific knowledge. The system then assists with document summarization, clause extraction, precedent identification, and compliance checking—all without exposing client confidential information to public AI services. This capability is particularly valuable for due diligence processes, contract analysis, and regulatory compliance documentation where information leakage could have severe consequences for clients.
Healthcare and Medical Research: Healthcare organizations use PrivateGPT for patient data analysis, treatment recommendations based on historical medical data, pharmaceutical regulatory document processing, and clinical research support. The system can analyze medical records to assist in diagnosis or recommend treatment plans based on historical data, all while ensuring HIPAA compliance and patient confidentiality. A medical device company using PrivateGPT for regulatory documentation reported accelerated FDA approval processes through intelligent document gathering while maintaining complete data sovereignty over clinical trial data.
Financial Analysis and Reporting: Financial institutions deploy PrivateGPT for transaction analysis, fraud detection, risk assessment, and regulatory reporting. The system can identify suspicious patterns in transaction data without exposing that data to cloud providers, enabling both security and performance improvements. Financial services firms processing over 2.3 million daily document queries for high-volume processing combined with cloud APIs for complex risk analysis (50K weekly queries) report achieving 60% cost reduction versus pure cloud while maintaining 98% of GPT-4’s effective quality.
Government and Citizen Services: Government agencies use PrivateGPT to answer citizen queries accurately and in multiple languages, simplify application procedures, and support employees by providing specific information in real time. This application is particularly valuable in India’s context, where government agencies increasingly need to provide AI-assisted services while maintaining strict data protection standards and ensuring citizen information remains within government infrastructure.
Customer Support and Knowledge Management: Organizations deploy PrivateGPT to provide accurate, contextualized answers to customer queries based on proprietary documentation, reducing employee workload and improving response times while maintaining complete control over customer data. Unlike cloud-based chatbots that might share your customer queries with third parties, PrivateGPT ensures all customer interactions remain confidential and never contribute to external model training.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Deploying PrivateGPT requires careful consideration of infrastructure requirements, hardware constraints, and technical expertise. The most significant challenge is understanding the spectrum of trade-offs between capability, cost, and technical complexity.
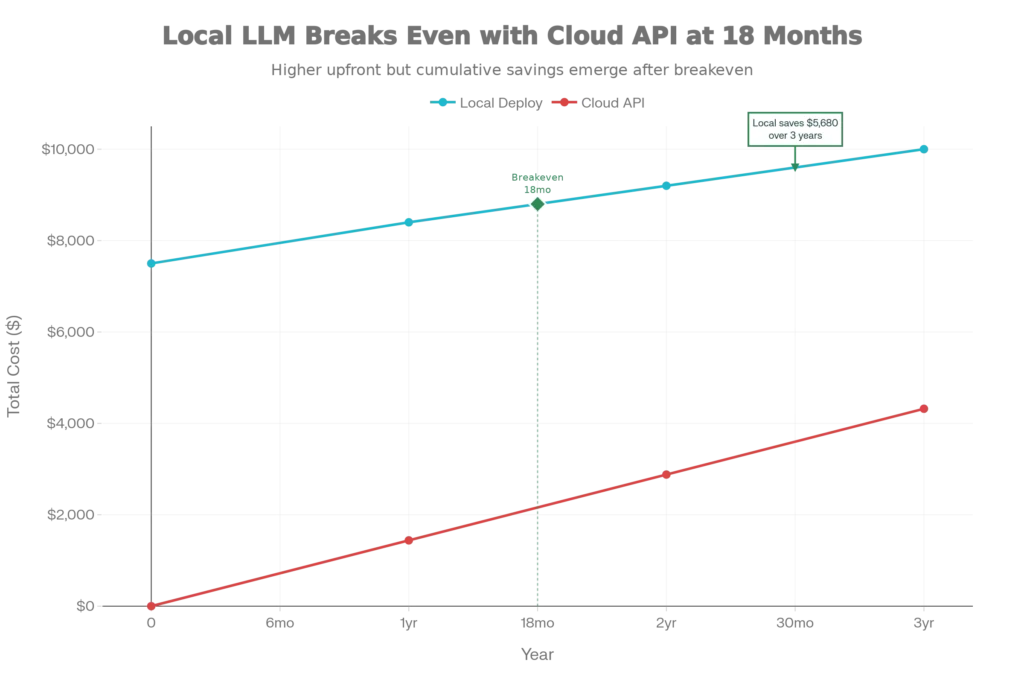
Hardware Requirements: The computational demands of running language models locally directly correlate with model size and capability. Entry-level deployments capable of running 7-billion parameter models require GPUs with at least 6GB VRAM (such as NVIDIA GTX 1660) and 16GB system RAM. These configurations cost $400-600 and deliver reasonable performance for general-purpose tasks but may struggle with complex reasoning. Mid-range deployments targeting 13-billion parameter models need GPUs like the RTX 3060/3070 with 32GB RAM, representing a $600-1,000 investment that handles most business use cases comfortably. Enterprise deployments requiring 40+ billion parameter models demand high-end GPUs (RTX 4080/4090) with 64GB RAM, representing a $1,500-2,000+ investment for research-grade performance.
The critical insight is understanding when local deployment achieves break-even economics with cloud services. Organizations processing more than 10,000 requests monthly achieve significant ROI within 3-12 months of local LLM deployment, while operational benefits extend far beyond cost savings. For organizations with high usage (100K+ requests/month), high data sensitivity, and low latency requirements (<200ms), local deployment offers the best balance of cost efficiency, privacy protection, and performance consistency.
Model Selection and Optimization: Open-source LLM performance has dramatically improved, with models from 2025 reaching 85-95% of GPT-4 performance, while local inference speed improved 2-5x through quantization advances and optimized frameworks. This means you no longer sacrifice significant capability by choosing local deployment. Quantization techniques—using 4-bit or 8-bit precision instead of full 32-bit floating point—reduce model size by 75-90% while maintaining acceptable accuracy. For example, a 70-billion parameter model quantized to 4-bit precision requires only 35GB of VRAM instead of 280GB, making enterprise-grade capabilities accessible on standard hardware.
Model Fine-Tuning and Domain Adaptation: For organizations with specialized domains (legal, medical, financial), fine-tuning a base model with domain-specific documents dramatically improves answer quality. The legal advisory firm case study achieved superior results by fine-tuning a smaller model with thousands of legal documents and templates rather than deploying a massive generic model. This approach combines the benefits of domain expertise with local deployment efficiency.
Integration with Existing Systems: PrivateGPT’s FastAPI-based architecture makes it straightforward to integrate with existing applications through standard REST APIs. The system can be deployed within private cloud environments (AWS, Azure, GCP with private subnets), on-premises data centers, or even on developer laptops for prototyping. This flexibility enables organizations to start small with proof-of-concept deployments and scale to enterprise systems without fundamentally rearchitecting their infrastructure.
Operational Challenges: The most underestimated operational cost involves expertise and ongoing maintenance. Unlike cloud services that handle updates automatically, locally deployed systems require your team to manage model updates, monitor hardware health, and troubleshoot integration issues. However, organizations with existing data engineering or machine learning teams typically find these operational requirements manageable once initial deployment is complete.
Setting Up PrivateGPT: Technical Implementation Guide
Setting up PrivateGPT involves several clear steps that organizations with intermediate technical capability can execute independently. The process begins with environmental setup and progresses through model deployment and integration.
Environment Preparation: Start by installing Python 3.10 or later and a package manager like Anaconda or Conda for managing dependencies. Clone the PrivateGPT repository from GitHub, which provides the core framework and example implementations. The installation process requires standard packages including transformers (for model access), torch (for PyTorch deep learning framework), fastapi (for the API server), and uvicorn (for serving the API).
Model Selection and Download: Download an open-source LLM model—GPT4All, Mistral, or Llama 2 are popular choices—in GGUF format (a quantized format optimized for local deployment). For production deployments, consider using model managers like Ollama or LM Studio, which handle model downloading, quantization, and optimization automatically.
Vector Database Configuration: Set up a local vector database by installing ChromaDB (simplest option), Milvus, or self-hosted Pinecone. Configure the database to store embeddings generated from your documents. ChromaDB requires minimal configuration and works well for organizations starting with PrivateGPT.
Document Ingestion: Create a simple ingestion pipeline using Python scripts that: (1) read documents from designated folders, (2) break them into chunks using LlamaIndex or similar libraries, (3) generate embeddings using a local embedding model, and (4) store embeddings with metadata in the vector database. This process happens once during setup and occasionally when adding new documents.
API Deployment: Deploy the PrivateGPT FastAPI server on your infrastructure using uvicorn or containerized deployment (Docker). The API mimics OpenAI’s interface, enabling you to swap between local and cloud endpoints with minimal code changes. This architecture supports multiple downstream applications—web interfaces, mobile apps, enterprise integrations—all connecting to your private, secure infrastructure.
Testing and Optimization: Test the system’s accuracy by asking questions across your document corpus and evaluating answer quality. Experiment with different chunk sizes, embedding models, and language models to find the optimal balance for your use case. Most organizations achieve production-ready performance within weeks of initial deployment.
Advanced Security Enhancements for Enterprise Deployments
Organizations handling highly sensitive data—pharmaceutical companies with clinical trial data, financial institutions with customer records, law firms with attorney-client privileged communications—can implement advanced security measures that provide mathematical guarantees of privacy protection.
Homomorphic Encryption: This cryptographic technique allows computations to occur on encrypted data without requiring decryption at any point in the process. An organization using homomorphic encryption could encrypt its entire document corpus, upload encrypted vectors to a vector database, and perform similarity searches entirely on encrypted data. The retrieved encrypted contexts would be decrypted only at the final response generation step, limiting exposure of individual documents to the language model. While homomorphic encryption adds significant computational overhead (typically 1,000-10,000x slowdown), it provides provable protection against unauthorized data access.
Secure Multi-Party Computation (SMPC): This technique distributes the AI processing across multiple servers such that no single server can access the complete data or intermediate results. For example, document embedding could occur on one server, vector storage on another, and language model inference on a third, with all servers collaborating securely without any individual server knowing the full context. This approach is particularly valuable for consortium arrangements where multiple organizations want to leverage shared AI capabilities without trusting any single party.
Differential Privacy: This mathematical technique adds carefully calibrated noise to data or model outputs, ensuring that no individual’s information can be extracted through inference attacks. A healthcare system implementing differential privacy in its PrivateGPT deployment adds noise to retrieved medical records before passing them to the language model, preventing the model from memorizing and reproducing specific patient information.
Role-Based Access Controls and Audit Logging: Enterprise deployments should implement granular access controls specifying which users can upload documents, query specific datasets, and access system logs. Comprehensive audit trails documenting every user action, query, and system change provide the accountability required for regulatory compliance and incident investigation. Organizations maintaining meticulous records aligned with these techniques achieve compliance with requirements like GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) or other regulatory standards requiring documented data handling.
Comparing PrivateGPT to Alternative Solutions
The landscape of private document processing tools includes PrivateGPT, LocalGPT, and various enterprise alternatives, each optimized for different use cases and user types.
PrivateGPT vs. LocalGPT: PrivateGPT is built around an API-first design that mimics OpenAI’s interface, making it suitable for developers building custom applications and integrating private AI into larger systems. LocalGPT is specifically tailored for individuals and researchers seeking a user-friendly, self-contained application for chatting with documents without development overhead. PrivateGPT’s modular architecture provides greater flexibility for experimenting with different embedding models and vector stores, while LocalGPT focuses on simplicity and out-of-the-box functionality.
PrivateGPT vs. Microsoft Copilot: Microsoft Copilot, when deployed in enterprise configurations, connects to organizational data in “a secure, compliant, privacy-preserving way” using Microsoft’s infrastructure. However, Copilot still relies on cloud connectivity through Microsoft’s services, introducing transmission risks absent in PrivateGPT’s fully local architecture. PrivateGPT provides greater independence from any cloud provider, making it superior for organizations requiring absolute control over data location and processing.
PrivateGPT vs. VectorShift and No-Code Platforms: Platforms like VectorShift offer enterprise-grade security (SOC 2 Type II, HIPAA, GDPR certifications) with no-code interfaces, making them accessible to non-technical users. However, VectorShift still involves some cloud processing through its platform infrastructure. PrivateGPT’s pure local deployment provides superior privacy guarantees at the cost of requiring technical implementation expertise.
Addressing Common Concerns and Misconceptions
Concern: “Local models can’t match cloud AI performance.” Reality: Open-source models have closed the performance gap dramatically. Mistral 7B, Llama 2 13B, and other 2025 models deliver 85-95% of GPT-4 performance on most tasks. For document understanding and question-answering—PrivateGPT’s primary use case—locally deployed models consistently match or exceed cloud alternatives. The performance gap only becomes apparent on highly specialized reasoning tasks or in-context learning scenarios where cloud models have training advantages.
Concern: “Local deployment requires computer science expertise.” Reality: Modern tools like Ollama, LM Studio, and AnythingLLM have dramatically lowered the technical barrier. A system administrator with basic command-line familiarity can deploy production-ready PrivateGPT systems. Pre-configured Docker containers further simplify deployment, and cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP) offer managed services that handle operational complexity while preserving local data processing.
Concern: “Hardware costs make local deployment prohibitively expensive.” Reality: This depends entirely on usage volume. For organizations processing fewer than 1,000 requests monthly, cloud APIs remain cost-effective. However, organizations spending more than $500 monthly on cloud API services typically achieve break-even on hardware investment within 6-12 months, making local deployment the economically rational choice. High-volume organizations processing 100,000+ requests monthly see payback periods of just 1-6 months.
Concern: “I’ll fall behind on AI capabilities without access to cutting-edge models.” Reality: Open-source models release on similar timelines to commercial alternatives, and you can update your deployed models as newer versions become available. PrivateGPT’s modular architecture enables switching between different models and embedding engines without system redesign. In practice, organizations find that domain-optimized smaller models outperform generic large models, and the ability to customize beats the appeal of marginally newer models.
The Future of Private, Secure AI
The trajectory of AI development increasingly favors privacy-first architectures. 40% of enterprises now run hybrid architectures—local models for routine tasks (85% of queries), cloud APIs for complex edge cases (15% of queries)—cutting costs 60% versus pure cloud while maintaining 98% of GPT-4’s effective quality. This hybrid approach represents the emerging best practice for organizations balancing privacy, cost, and performance.
Research advances in privacy-preserving AI continue to strengthen the case for local deployment. Techniques like differential privacy, federated learning, and homomorphic encryption are moving from academic concepts to production implementations, making advanced privacy protections accessible to organizations beyond those with specialized security expertise. The SSRN research paper on “Securing Retrieval-Augmented Generation” proposes frameworks integrating homomorphic encryption, secure multi-party computation, and robust access controls to minimize data exposure risks without compromising system performance.
Regulatory momentum also supports this shift. The Financial Data Privacy Act of 2024, strengthened GDPR enforcement, and HIPAA’s continuing dominance as healthcare’s regulatory standard all create pressure toward solutions providing stricter data localization. Organizations that deploy privacy-first architectures now position themselves advantageously for future regulatory changes, avoiding costly migrations later.
Read More:LM Studio Tutorial: Run Llama 3 on a Low-End PC – Complete 2025 Guide
Source: K2Think.in — India’s AI Reasoning Insight Platform.
